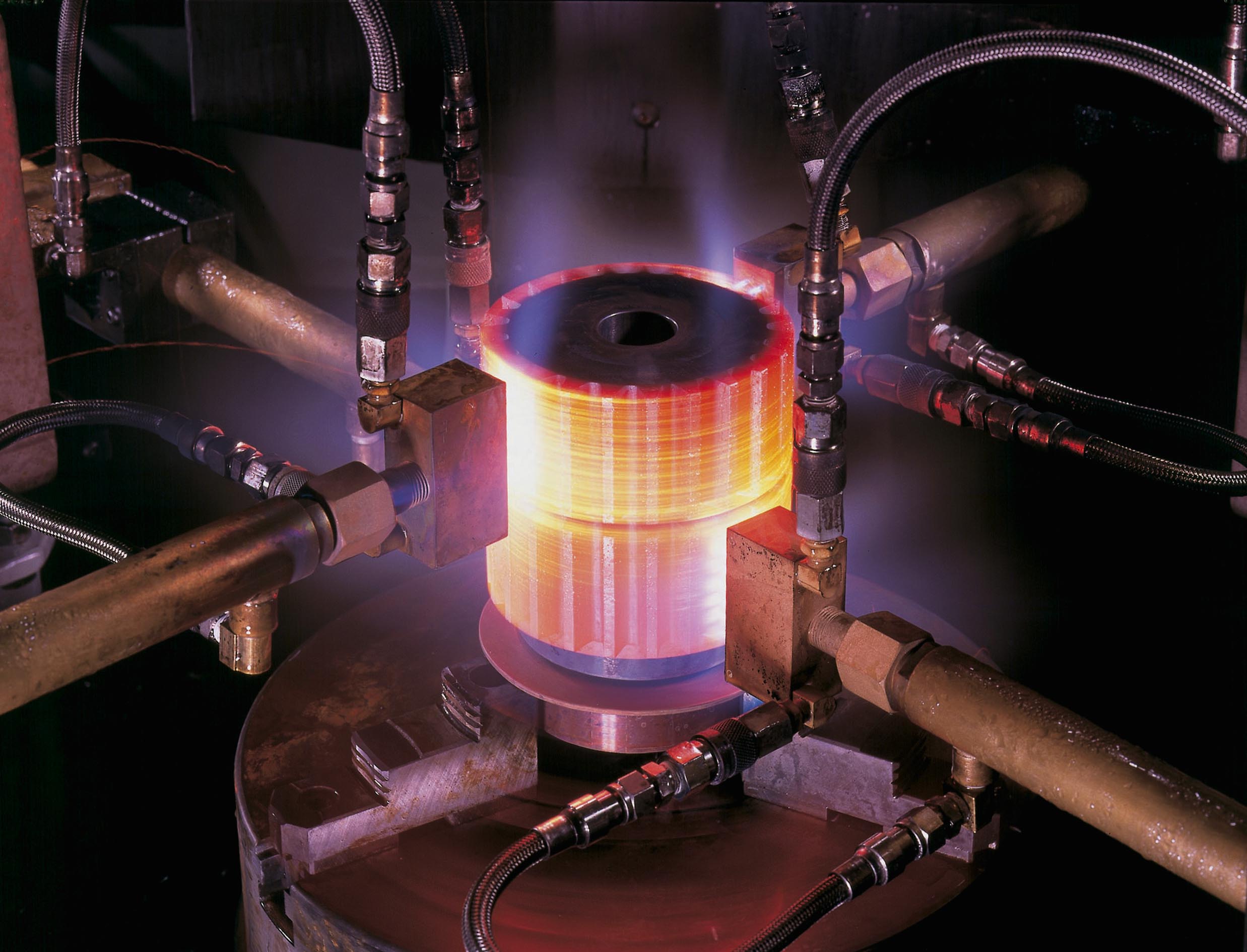
Heat Treatment Processes
October 31st, 2017Steel heat treatment is an essential process in numerous industries. It is the act of altering the chemical or physical properties of a substance, which most of the time is metal. Through the heating process, a piece of metal becomes malleable, allowing a professional to alter its physical appearance into the desired shape. To meet a wide range of demands, there are several different heat treatment process available. Some of which include: case hardening, oil quenching, tempering steel, and annealing steel. Each one has its own unique benefits and times when it is best used.
Vacuum Carburizing
Vacuum carburizing is very similar to plasma carburizing except this takes place in a vacuum furnace system. The gas used in this process is propane, and the furnace is set to a temperature usually in the range between 900° and 1,050° Celsius. The metal undergoes a diffusion state, which allows the metal to obtain a more desired carbon profile. A benefit of using this process is that the metal is altered in a protective environment. Therefore, it is not exposed to toxic off-gases or other forms of oxidation.
Gas Nitriding
Gas nitriding is most commonly used when a piece of metal needs to undergo a thermochemical alteration to make it more resistant to degradation. This makes the surface harder and extends the piece’s lifespan. This process is typically used on pieces of metal that are expected to receive a lot of wear and tear. It is useful for metal parts used in the loading and unloading of materials.
Oil Quenching
In the past, whenever a metal component underwent extremely hot temperatures, it would be treated with water afterward to serve as a quenching medium. While it is still used and effective, there is another method for accomplishing this using oil. This is referred to as oil quenching. Due to the fact oil is unable to boil as rapidly as standard H2O, the metal is able to retain the heat for longer. This process involves putting the component in a furnace set to a temperature in excess of 2,000°. After it has reached the desired temperature, it is placed in a tank filled with oil. With this method, there is a significant drop in the likelihood of unevenness, distortion and cracking.
Stress Relieving
When a piece of metal is cut or physically altered in some way, the internal body undergoes extreme stress. As a result, the piece is much more susceptible to breaking and other types of damage. However, this risk can be substantially reduced by having the piece undergo stress relieving. For effective stress relieving, the piece must be held at the same temperature for a specific amount of time.
The general rule of thumb to follow with this process is that the item should be exposed to an environment that is anywhere between 590° and 680° Celsius. Next, a professional needs to determine how large the piece is. The metal needs to remain at a consistent temperature for one hour per each inch of the metal’s thickness. At the end of the process, the item achieves greater dimensional stability.
Vacuum Brazing
When most people think about two pieces of metal being joined together, they assume it is done via welding. While that is certainly a possibility, there is a more intricate process for more complicated treatments, and it is called vacuum brazing.
With this process, two pieces are joined together using a filler piece. For best results, the temperature of the brazing device itself needs to be lower than the melting point of each of the two pieces of metal. To complete this process, the component needs to be placed in a vacuum furnace to create an environment where contamination is significantly reduced.
Carbonitriding
Carbonitriding is another process of making pieces of metal more resilient against normal wear and tear. However, this treatment is most often used on low-quality pieces of metal to give them the same durability as a higher grade of steel.
It has many similarities to carburizing, but in general, it is far less likely to undergo softening during the process. This process is particularly useful on gear teeth, dies, tools, fasteners, and bearings.
Bright Hardening
Bright hardening is most often used in instances where the person wants the metal to retain a bright finish at the end of the project. This is considered an annealing process in heat treatment where the metal is both cooled and heated in a static environment. Through this, oxidation becomes inhibited. Screw machine parts, springs, stamping and investment castings often need to go through this treatment.
Picking between the different heat treatment process can be a hassle. The best treatment for a part ultimately comes down to what exactly it is and what it is intended to be used for. Each different heat treatment process has its place.
Make sure to use the right one whenever you require heat treatment so that you receive the most benefits out of your parts. Specialty Steel Treating can assist you with choosing between each different heat treatment process and purchasing the right steel heat treatment. Contact us for a quote.